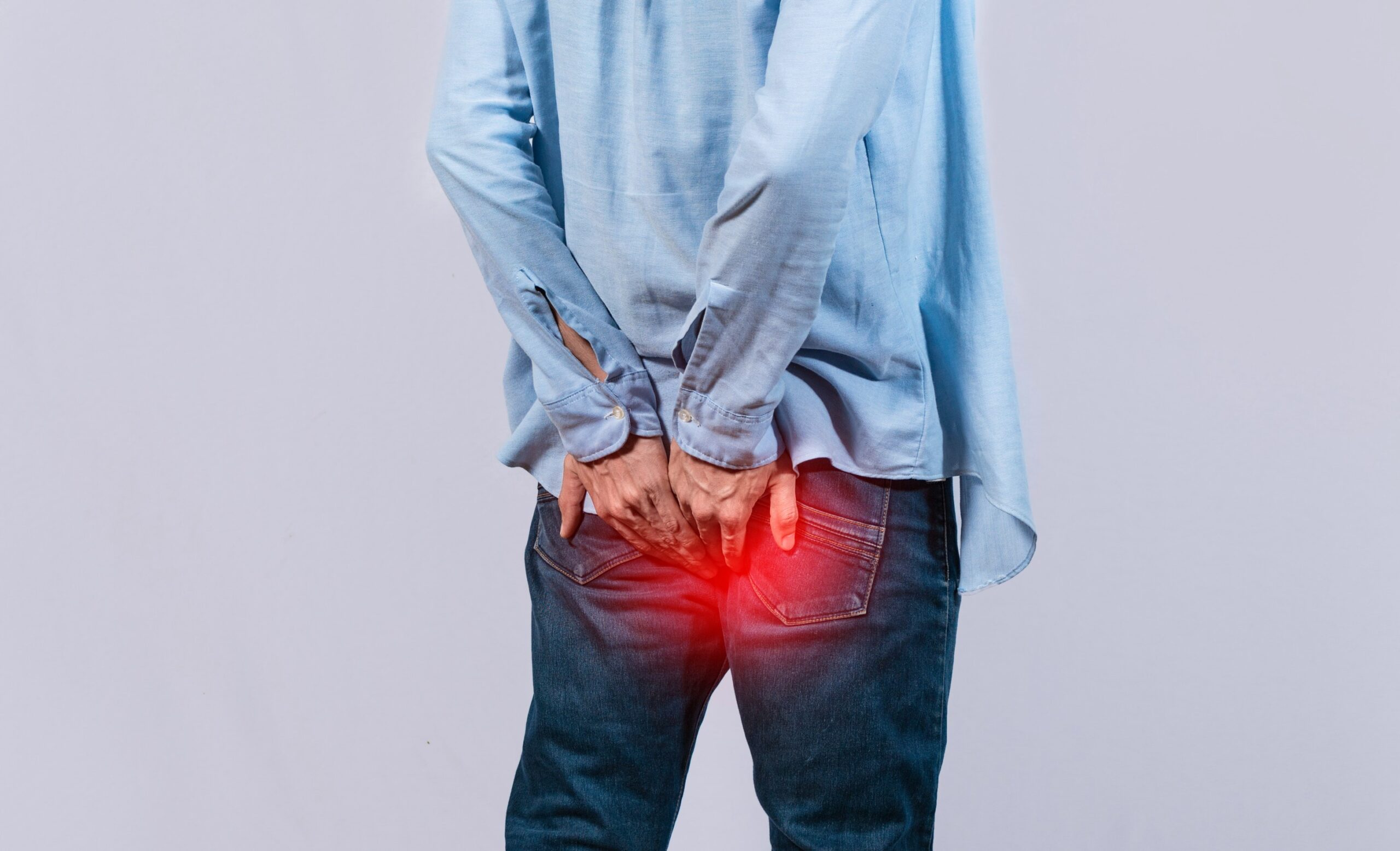
You must all be familiar with constipation – the silent struggle that turns even the mightiest into bathroom philosophers! It’s a widespread gastrointestinal issue, which brings in a lot of discomfort and health risks. It affects people of all ages and can be caused by various factors, including a lack of fiber in the diet, dehydration, sedentary lifestyle, or certain medications. Symptoms usually include straining during bowel movements, hard or lumpy stools, bloating, and discomfort. While occasional constipation is normal, ignore it too long and it may lead to severe conditions like Hemorrhoids, anal fissures, rectal prolapse and such.
Some most common constipation management strategies include dietary changes, increased water intake, probiotics, and regular exercise. But apart from these, fiber supplements provide a widely accepted remedy, crucial for effective management. But what exactly are fiber supplements and how do they help? Let’s find out!
What are Fiber Supplements?

First of all, as you may know, fiber is a type of carbohydrate found in plant-based foods. It’s indigestible, passing through the digestive system relatively intact and this characteristic gives fiber its ability to promote digestive health. Fiber supplements are concentrated forms of fiber derived from plants or synthetic sources. These supplements provide a convenient way to increase fiber intake when dietary sources are insufficient. Their concentrated nature ensures a potent dose of fiber, addressing deficiencies or specific health goals. Also, fiber supplements often undergo processing to remove excess sugars and calories, making them suitable for various dietary plans. With their accessibility and effectiveness, they serve as valuable allies in promoting digestive health and overall well-being. They come in various forms such as powders, pills, or chewable tablets. Let’s talk about that in detail for a moment.
Various Types of Fiber Supplements

There are two main types of fiber: soluble and insoluble. Soluble fiber dissolves in water to form a gel-like substance, while insoluble fiber adds bulk to stool, aiding in its passage through the digestive tract. Aside from them, fiber supplements come in various types:
- Psyllium Husk: Derived from the seeds of the Plantago ovata plant, it forms a gel-like substance when mixed with water, aiding in softening stool.
- Methylcellulose: This insoluble supplement adds bulk to stool, facilitating its passage through the digestive tract.
- Calcium Polycarbophil: It functions similarly to methylcellulose by bulking up stool and is often recommended for individuals with sensitive digestive systems.
- Wheat Dextrin: Derived from wheat starch, it is a soluble fiber supplement that softens stool without causing excessive gas or bloating.
- Inulin: Extracted from chicory root or other plants, Inulin serves as a prebiotic, nourishing good bacteria and promoting a healthy gut microbiome.
- Glucomannan: It is a soluble supplement that forms a gel-like substance and promotes feelings of fullness hence, also aiding in weight management.
Each type of fiber supplement has its unique characteristics and may be suitable for different individuals based on their specific needs and preferences. So, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
The Role of Fiber Supplements

By now you must have already decoded most of the importance and role of fiber supplements. So, following are some of the most crucial ones:
- Fiber supplements add bulk to stool, making it easier to pass and preventing constipation.
- Soluble supplements absorb water, softening stool and easing bowel movements.
- They aid in regulating bowel function, promoting healthy digestion, and preventing gastrointestinal issues.
- They also act as prebiotics, nourishing beneficial gut bacteria and supporting a healthy microbiome.
- Fiber supplements help stabilize blood sugar levels by slowing down sugar absorption, reducing the risk of diabetes.
- Some fiber supplements, particularly soluble fiber, can lower LDL cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart disease.
- Fiber supplements promote satiety and help control appetite and manage weight effectively.
Aside from all this, high fiber intake from supplements may also reduce the risk of colon cancer by promoting regular bowel movements and eliminating toxins. However, consuming fiber also has its own set of factors you need to consider.
How to Choose and Consume Fiber supplements?

First of all, when selecting a fiber supplement, consider factors such as the type of fiber, dosage, and form. It’s essential to start with a low dosage and gradually increase intake to avoid bloating or gas. Secondly, drink a lot of water! Water helps fiber move through the digestive tract smoothly and prevents dehydration. Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water per day, especially when increasing fiber intake. Lastly, fiber supplements can cause side effects such as bloating, gas, and abdominal discomfort, particularly when first starting. These symptoms usually subside as the body adjusts to increased fiber intake.
To conclude, fiber supplements play a crucial role in promoting digestive health and alleviating constipation. Incorporating them into a balanced diet can provide numerous benefits for overall well-being. So, here’s to fiber supplements: the unsung heroes of happy bellies and smoother days ahead!
REFERENCES
1. Mayo Clinic – https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/expert-answers/fiber-supplements/faq-20058513
2. John Hopkins Medicine – https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/constipation#:~:text=Constipation%20is%20a%20condition%20in,than%20three%20times%20a%20week.
3. WebMD – https://www.webmd.com/diet/compare-dietary-fibers
4. Harvard Tech – https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/carbohydrates/fiber/
5. NIH – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5413815/
6. CDCP – https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/library/features/role-of-fiber.html
7. Medical New Today – https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/146935
FAQ’s
Q. Is fiber good for the Kidneys?
A. Fiber plays a role in supporting kidney health by aiding in the management of conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure, which are risk factors for kidney disease. Additionally, fiber promotes regular bowel movements, reducing the burden on the kidneys by helping eliminate waste products efficiently.
Q. What is a good fiber supplement?
A. Psyllium husk is a widely recommended fiber supplement due to its high soluble fiber content. It helps soften stool, promotes regular bowel movements, and supports overall digestive health.
Q. When should I take fiber supplements?
A. Fiber supplements can be taken at any time of day, preferably with plenty of water. Some people prefer taking them with meals to aid digestion, while others find it convenient to take them at separate times to ensure consistent intake.
Q. Is fiber better in pills or powder?
A. Honestly, it depends on personal preference. Pills offer convenience, while powders can be easily mixed into beverages or food for versatility.
Q. Is it OK to take fiber everyday?
A. Yes, it is generally safe and recommended to consume fiber daily as part of a healthy diet. Adequate fiber intake supports digestive health, regulates bowel movements, and may lower the risk of certain health conditions. However, it’s essential to drink plenty of water when increasing fiber intake to prevent potential digestive discomfort.
Q. Can too much fiber be harmful?
A. Excess of anything is bad. Similarly, over consumption of fiber can lead to bloating, gas, abdominal discomfort, and diarrhea. It’s essential to gradually increase fiber intake and drink plenty of water to prevent potential digestive issues.